Analysis of common gear drive faults
(1) Manufacturing errors
The manufacture of gears usually produces eccentricity, circumferential error, base joint error, tooth shape error and several other typical errors. There are many reasons for these errors, including errors from the machine tool movement, errors in the cutting tool, the tool, the workpiece, improper installation and commissioning of the machine system, errors in the fixture and internal stresses caused by heat treatment of the gear deformation.
When the gears of these errors are large, it will cause the gear drive slow and fast micro-inertia interference with the rotation, so that the gear vice mesh when the impact, vibration, causing greater noise.
(2) Assembly errors
Due to the assembly technology and assembly methods, usually in the assembly of gears will cause "one end contact, one end overhang" assembly error; gear shaft straightness deviation (coaxiality, alignment error) and gear imbalance.
One end contact or gear shaft straightness deviation will cause the gear to bear uneven load, resulting in overloading of individual gear teeth causing local early wear, and in serious cases even causing the gear teeth to break. The unbalance of the gears will cause shock vibration and noise.
(3) Faults arising during operation
1. Tooth surface plastic deformation. When the gear material is soft and the transmission load is large, easy to produce tooth surface plastic deformation. Under the action of excessive friction between the tooth surface, the tooth surface contact stress will exceed the material extrusion yield limit, the tooth surface material into the plastic state, resulting in the plastic flow of the tooth surface metal.
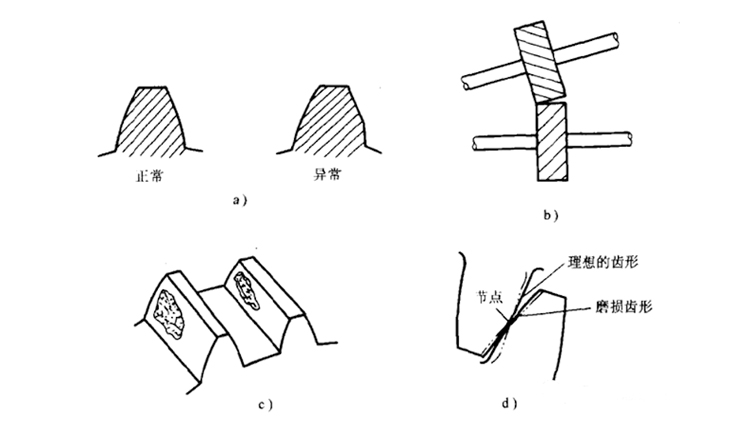
This results in the active gear forming a concave groove on the tooth face near the pitch line and the driven gear forming a convex rib on the tooth face near the pitch line, thus destroying the tooth profile.
Sometimes "flying edge burrs" can also appear on the driven tooth surface of certain types of gears. Severe extrusion of metal metal filled with top gap, can cause violent vibration, or even bending or fracture, affecting the normal gear mesh transmission.
2. Fracture of the gear teeth. When gear transmission, the force of the active gear and the reaction force of the driven gear are acting on each other's gear teeth through the contact point, the most dangerous situation is that the contact point is located at the top of the teeth of the gear teeth at a certain moment; at this time, the gear teeth are like a cantilever beam, the bending stress generated by the root of the gear teeth is the largest, if the sudden overload or impact overload, it is easy to produce overload fracture at the root of the teeth.
Even if there is no impact overload force conditions, when the wheel teeth under alternating load generated by the phenomenon of alternating stress concentration, but also prone to fatigue cracking; gradually expand, resulting in the wheel teeth at the root of the tooth fatigue fracture.
Fractures may also occur in any part of the tooth due to manufacturing and installation errors, quenching cracks, damage from grinding cracks and excessive thinning of tooth thickness after severe wear.
3. Tooth surface fatigue. The so-called tooth surface fatigue mainly includes tooth surface pitting and spalling. The cause of pitting is mainly due to microscopic fatigue cracks caused by pulsating changes in contact stress on the working surface of the gear teeth, when the lubricant enters the surface crack area and then closes the entrance and then extrudes during the meshing process.
The lubricant in the microscopic fatigue crack area expands the cracked area of the tooth surface under high pressure, causing the surface metal particles to fall off the tooth surface, leaving a small pit to form tooth surface pitting. When the fatigue crack on the tooth surface continues to expand to a deeper, more distant, or make a series of small pits between the material failure and connected, resulting in a large area or large off the phenomenon formed the tooth surface spalling.
4. Tooth surface wear or scratches. Gear teeth in the process of meshing transmission there is relative sliding, coupled with poor lubrication, lubricating oil is not clean, lubricant deterioration, low speed heavy load or heat treatment quality is poor, etc., can cause the gear teeth tooth surface adhesion wear, abrasive wear, corrosion wear and scratches.
For the gear transmission process failure, should be from these three points of comprehensive analysis, to find out where the fault lies. The production of gears requires a high degree of numerical accuracy, which may lead to the production of unqualified gears and scrap due to a small error, resulting in losses, so the staff must be fully focused on the production of gears to reduce unnecessary errors.
- Previous:Already the first article
- Next:Gearing noise reduction measures