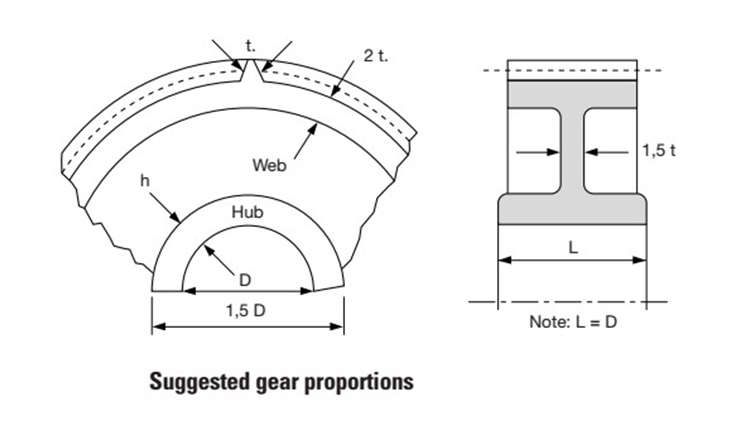
Plastic gear mould design structural elements
Plastic moulding is the abbreviation for a combination of moulds used for compression, extrusion, injection, blow moulding and low foaming moulding. The coordinated variation of the mould's convex and concave moulds and auxiliary forming systems allows a range of plastic parts of different shapes and sizes to be processed.
The latest development in plastic moulding is the direct connection between the external computer and the CNC machine tool via the RS-232C serial port for fast and accurate transmission of NC programs directly, and the external computer can be connected to multiple CNC machine tools with the same or different control systems for information sharing, and can manage the information in the production process within the CNC section consisting of multiple machine tools to reduce the production preparation, especially the preparation time of the NC program.
I. Description of the structural elements to be considered in the design of precision plastic gear moulds.
1. The parting surface, i.e. the contact surface where the concave and convex moulds fit together when the mould is closed. Its position and form are influenced by the shape and appearance of the product, wall thickness, forming method, post-processing process, mould type and structure, demoulding method and moulding machine structure.
2、Structural parts, i.e. slider, slant top, straight top block of complex moulds, etc. The design of structural parts is very critical, which is related to the life of the mould, processing cycle, cost, product quality, etc. Therefore, the design of the core structure of complex moulds requires a high comprehensive ability of the designer to pursue a simpler, more durable and more economical design solution as far as possible.
3, mold accuracy, namely avoid card, fine positioning, guide pillar, positioning pin, etc.. Positioning system is related to the appearance quality of products, mould quality and life, according to different mould structure, choose different positioning methods, positioning accuracy control mainly rely on processing, internal mould positioning is mainly the designer to fully consider, design a more reasonable and easy to adjust the positioning method.
4, pouring system, that is, from the injection molding machine nozzle to the cavity between the feed channel, including the main flow channel, diversion channel, gate and cold material cavity. In particular, the location of the gate should be selected to facilitate the molten plastic in a good flow state filled cavity, attached to the product of the solid runner and gate cold material in the opening of the mould is easy to eject from the mould and be removed (except for hot runner mould).
5, plastic shrinkage rate and the impact of the product size accuracy of precision mould processing of various factors, such as mould manufacturing and assembly errors, mould wear and tear, etc.. In addition, the design of compression moulds and injection moulds, should also consider the matching of the process and structural parameters of the forming machine. Computer-aided design techniques have been widely used in the design of precision plastic gear moulds.
The main objective of semi-finishing is to make the workpiece contour shape flat and the surface finishing margin uniform, which is particularly important for tool steel moulds, as it will affect the variation of the cutting layer area of the tool and the tool load during finishing, thus affecting the stability of the cutting process and the quality of the finishing surface.
The plastic mould optimisation process includes the calculation of the roughing profile, the calculation of the maximum remaining machining allowance, the determination of the maximum allowable machining allowance, the partitioning of the profile where the remaining machining allowance is greater than the maximum allowable machining allowance (e.g. recesses, corners and other areas where the transition radius is less than the radius of the roughing tool) and the calculation of the tool centre trajectory during semi-finishing machining.